Solar Decathlon 2017
/I visited the Solar Decathlon in Denver this weekend, where 11 houses designed and built by students are on display. Although I have been a bit critical of the Decathlon, both in The Solar House and here on the blog, I have the highest regard for the students' talents and efforts.
And this Decathlon is different, because Denver will be a bit cold this coming week during the period that the houses will be measured for energy use. A few of the houses are clearly designed for passive solar gains.
Here are some photos of the 12 houses. More info can be found at the Department of Energy's Solar Decathlon website.
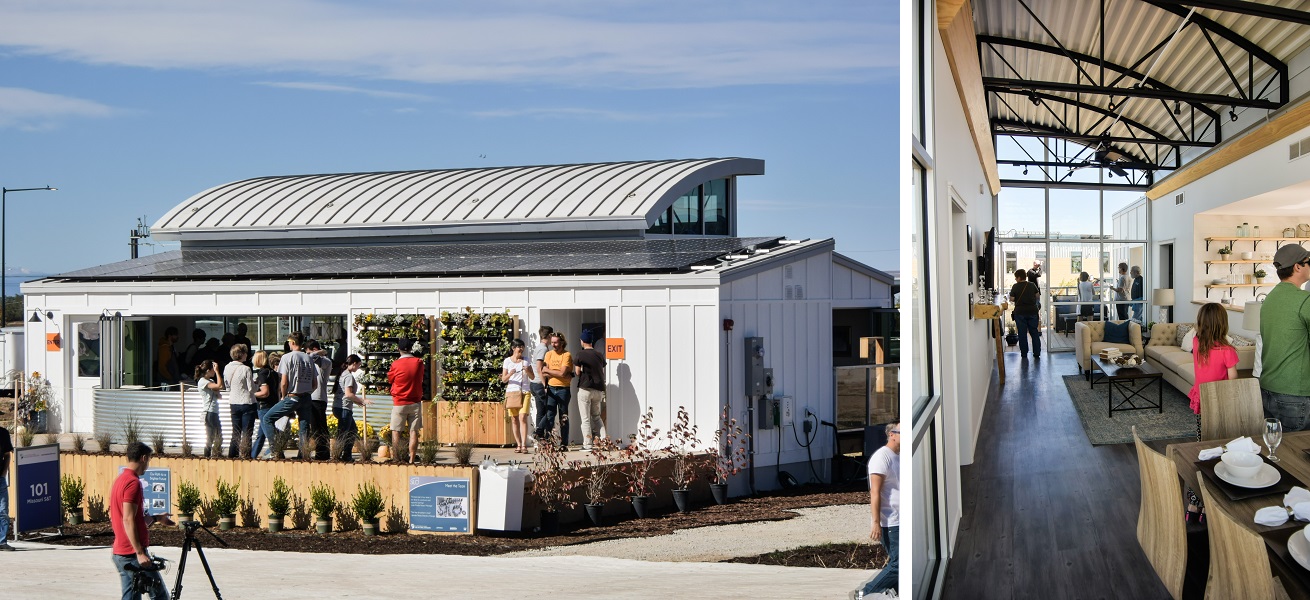
Smart Innovative Living Oasis (SILO) by Missouri S&T
team website
Our H2Ouse by University of California, Davis
team website
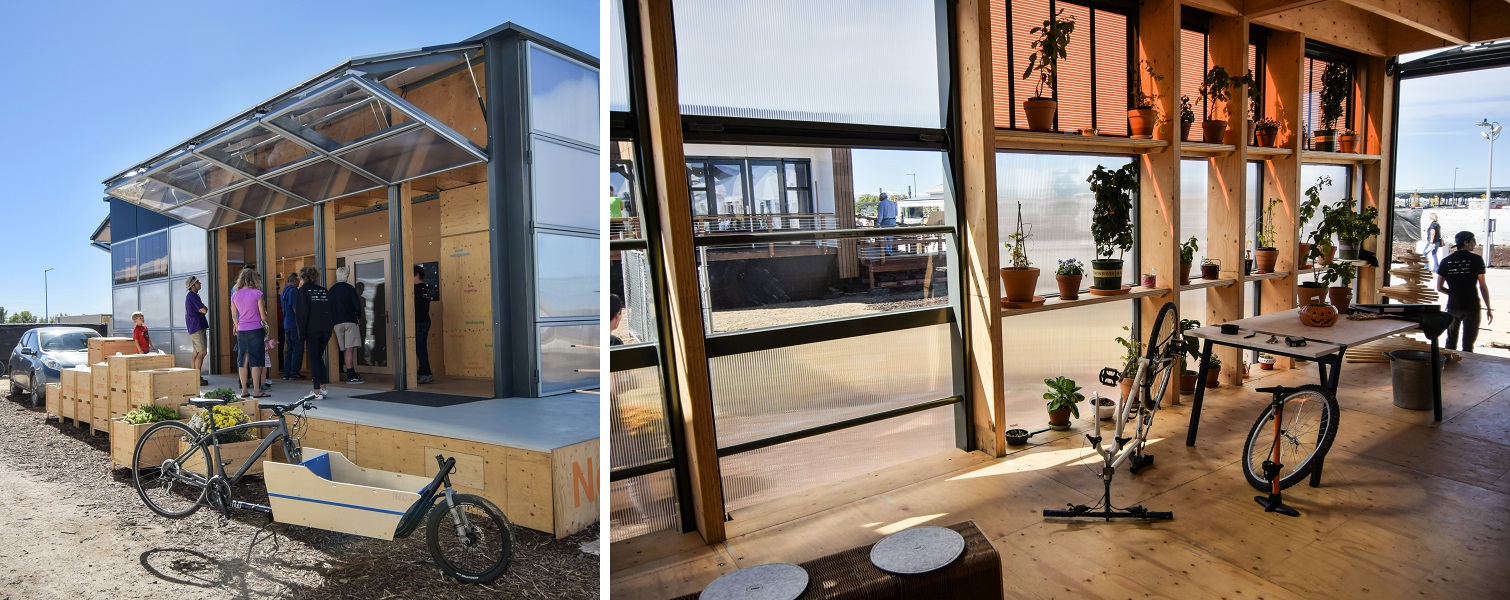
Resilient Adaptive Climate Technology (reACT) by University of Maryland
team website
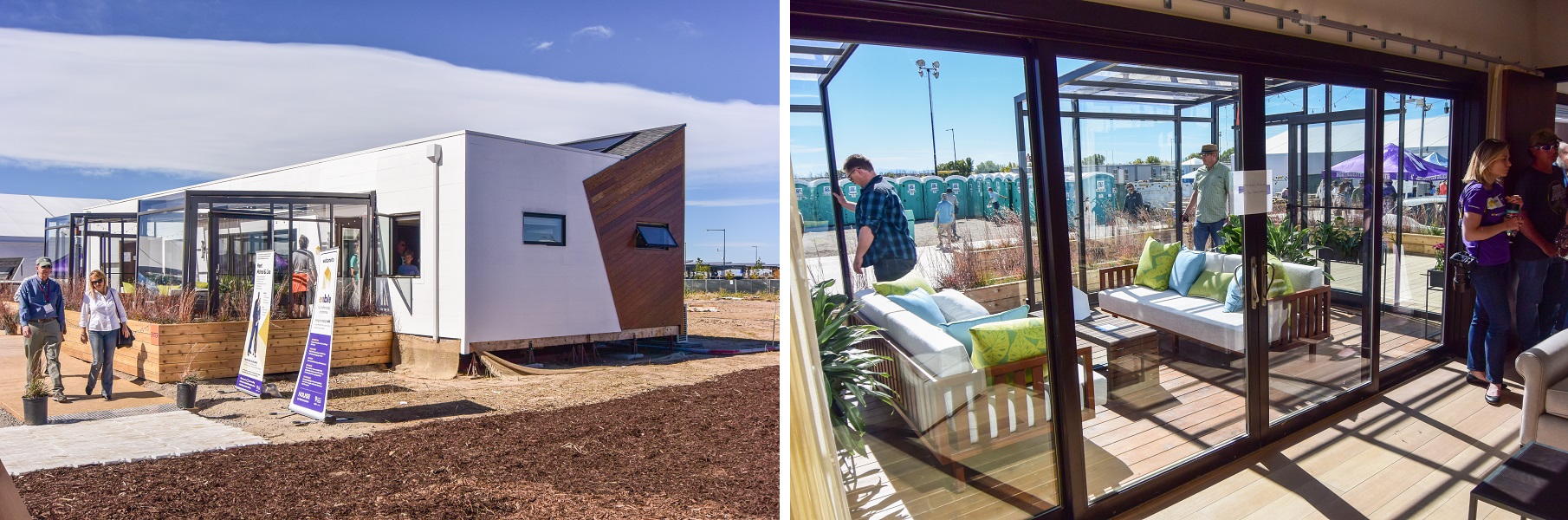
RISE house by University of California, Berkeley and University of Denver
team website
Selficient by HU University of Applied Science, Utrecht, Netherlands
team website
NeighborHub by Swiss Team
team website
Enable by Northwestern University
team website
CRETE house by Washington University, St. Louis
team website
surviv(AL) House by Team Alabama
team website
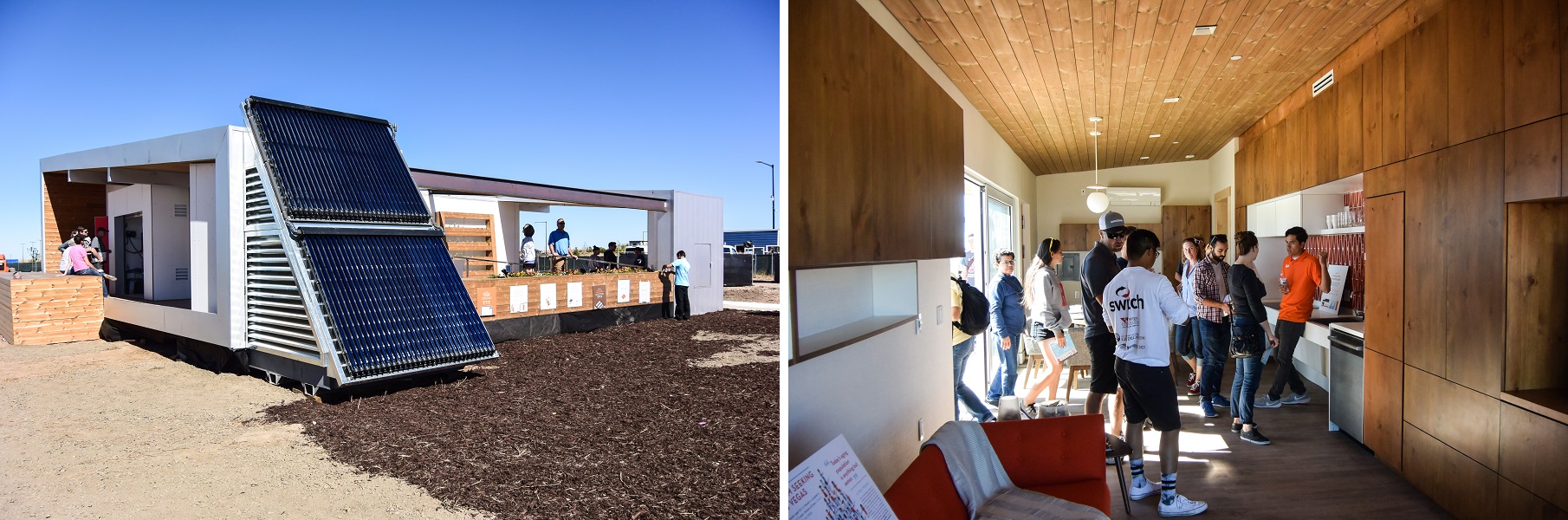
Sinatra Living by University of Nevada, Las Vegas
team website
BEACH House by Team Daytona Beach
team website
While I am glad the contest is being held in a cold-climate city, to reward passive solar heating, the chosen site in Denver—undeveloped suburbia—is a difficult one for showcasing the event. I noticed students walking approximately 2 miles across vacant land to their lodgings at airport hotels. This is a typical view when approaching the event.
(Edited to add: This area is planned to be a Net-Zero eco-district called Peña Station NEXT.)
In any case, I liked many of the houses very much and enjoyed talking to the students. Good luck to all of them!